THERE ARE OTHER THINGS to be said: another novel of Frederic Tuten's just read (Tallien: A Brief Romance, which made me think of Georges Perec's W, or the Memory of Childhood more than once. The Met "live-in-theater" production of Shostakovich's opera Nose, which in spite of William Kentridge's mise-en-scene, or perhaps because of it, seemed less diverting to me than the production seen last January in Rome, and reported here. (Search it if you like in the little box up at the left.)
Mark di Suvero's marvelous sculpture at Crissy Field. The fabulous road across the mountains from Buttonwillow to Ojai. The big exhibition of Richard Diebenkorn's Berkeley paintings.
And in the next month, a show of paintings by the late Kenjilo Nanao; a hearing of Robert Erickson's marvelous string quartet Corfu, and three plays to be seen down in Pasadena: The Guardsman, Endgame, and Pericles.
But this next month is November, and I've decided to dedicate it to a completely different project. So let's all take a break, and I'll be back December 1, maybe with a cursory retrospective catch-up.
Thursday, October 31, 2013
Music in space
 LAST SATURDAY WE HEARD Lisa Bielawa’s Crissy Broadcast, the San Francisco variant of a piece she wrote for performance at Berlin’s old Tempelhof Airfield last May. Crissy Field, on the north shore of the Presidio, is a retired airstrip, like Tempelhof, but considerably smaller, and grass instead of tarmac, and it would have been fascinating to have been able to compare the performances, but budgets are small around here, and I’m no longer paid to cover such events. (Nor have I ever been to Berlin; nor do I want to go there.)
LAST SATURDAY WE HEARD Lisa Bielawa’s Crissy Broadcast, the San Francisco variant of a piece she wrote for performance at Berlin’s old Tempelhof Airfield last May. Crissy Field, on the north shore of the Presidio, is a retired airstrip, like Tempelhof, but considerably smaller, and grass instead of tarmac, and it would have been fascinating to have been able to compare the performances, but budgets are small around here, and I’m no longer paid to cover such events. (Nor have I ever been to Berlin; nor do I want to go there.)Bielawa chose the title [Airfield] Broadcast for its allusion not to radio or television but to the sowing of seed, as it is broadcast — strewn broadly and evenly — across a field, whether from machine or hand. (I remember with pleasure striding across the plowed and harrowed damp field, a bucket in my left hand, dipping my right hand into the grain, then strewing it, palm up, grain flying out between index finger and thumb. There are so many subtle controls in that hand, affecting the amount and pattern of the distribution, and what a blend of sight, smell, touch, even sound…)
The San Francisco installation was (as I understand it; I've done no real research) produced with the collusion of the San Francisco Contemporary Music Players and other — perhaps many other — ensembles. The first person I met when we arrived on the scene, a little before ten o'clock, was Roy Malan, the principal violinist with the SFCMP. He was there leading a sizable contingent of musicians from I forget what high school; and it turned out many SFCMP stalwarts were doing the same.
 There was Willie Winant, for example, leading musicians from St. Mary's, including a snare drummer who turned out to be the son of acquaintances of ours, with whom we lunched after the performance. A little later I ran across Peter Josheff, clarinetist with the contemporary ensemble Earplay.
There was Willie Winant, for example, leading musicians from St. Mary's, including a snare drummer who turned out to be the son of acquaintances of ours, with whom we lunched after the performance. A little later I ran across Peter Josheff, clarinetist with the contemporary ensemble Earplay.The various ensembles ranged from small rather cohesive groups, like Winant's percussion ensemble, to full orchestras like Malan's. Toward the end of the hour I came upon an a capella chorus. In Berlin there were apparently even pianos, hauled around on motorized luggage carriers; but I saw no pianos, or harps or pipe organs or kettledrums, at Crissy Field: the grass worked well enough for lightweight biplanes at the time of World War One, but I doubt it would stand up to Steinways.
When I ran into Roy he was fiddling with an improvised lyre he'd mounted at the scroll end of his violin — tape of some sort holding a clothespin. As a band musician in my youth I remember all our wind instruments were fitted with such things. Only the flutists, their instruments sticking out sideways from the face, had to invest in special equipment: an armband with a couple of buckles to tighten it over the left forearm carried the lyre. We played from little sheets of music hardly bigger than a file card, but of course we were only playing Sousa marches or the like, with lots of repeat signs in them.

The parts, and the evidence that came to my ears, suggested that Crissy Broadcast is composed of a number of musical cells, short structural units, which are repeated a variable number of times, and are separated by silences apparently measured by the clock. I saw a number of leaders consulting wrist-watches, then signaling their ensembles before beginning to conduct.
I was told that the spatial distribution, which at first seemed set up more or less imprecisely but evidently according to a preconceived plan, was then affected by scored instructions for the musicians to walk a given number of paces, in a given direction.
Like many others in the audience I was so intent on photographing, maintaining silence, and enjoying the sounds and the atmosphere, that I found it impossible to observe the entire effect as a unit. If I were more disciplined I'd have gone to the composer's discussion of the event, after that morning performance, and then to the repeat performance in the late afternoon: but other pleasures interfered.
What did Crissy Broadcast sound like? To me, perhaps influenced by knowing of its German origin, it sounded a little Germanic. The preponderance of wind instruments (since after all string instruments don't make sounds that carry nearly as well out of doors) and percussion, and the repeated short "melodicles," as Lou Harrison calls these tunelets, brought to mind, for whatever reason, the music Kurt Weill provided for Bertolt Brecht's plays. Maybe Hindemith's gebrauchmusik is in the mix, too.
I also thought of Douglas Leedy's Exhibition Music, composed in 1965 for a backyard reception for, as I recall, people connected somehow with the twentieth anniversary of the founding of the United Nations. (You can hear Exhibition Music streaming online.) Leedy was writing in the spirit of Erik Satie's musique d'ameublement (furniture music), the first of which, composed in 1917, was in fact intended to be performed pour l'arrivée des invités (grande réception) - À jouer dans un vestibule (for the arrival of the guests (grand reception) - to be played in a vestibule).
But Bielawa's score is not in that spirit, I think. She, or someone writing for her on the website publicizing the event, refers to the work as "a massive, spatialized symphony involving more than 800 professional, student and amateur musicians, including orchestras, bands, and experimental new music groups," and that description brings to mind Charles Ives's Universe Symphony worked on from 1911 or so to 1928, when Ives stopped composing. I'm not sure I'd attach the word "symphony" to what I heard at Crissy Field on Saturday; to me the word suggests something both more determined as composition and more resolved in performance.
(I realize that etymologically the word simply means "sounds together," and there certainly were many sounds sounding simultaneously; but the word has accumulated some linguistic meaning, and it always seems unfortunate when words are dulled, deliberately or not.)
Instead, Crissy Broadcast seems to me to fall into a different category, if indeed there are enough such pieces to form a category: it is landscape music. Not background music to cover awkward pauses (or generalized chatter) in a social context, but music meant to accompany the theater that is landscape when it is observed or experienced for esthetic purpose.
One of the most pleasant aspects of Crissy Field is its generosity in admitting ambient sounds, and the San Francisco location was generous in providing them: occasional fog horns; the sound of the elevated highway that formed its southern backdrop; the lapping of the bay on the beach, if you were close enough and attentive enough to hear it. And, of course, occasional muted talk, though the audience seemed to me to be unexpectedly quiet and respectful. And, once or twice, a dog, barking in the distance.
The weather was glorious: a thin fog was lifting throughout the performance, veiling the magnificent Golden Gate Bridge, as if it were politely retiring in order to allow Mark di Suvero center stage, through the dozen or so marvelous huge steel sculptures of his currently installed at Crissy Field. I'm told that Saturday afternoon was cooler and windier, and Sunday noon downright cold and miserable. I'm glad we went when we did.
I made an eight-minute video, strolling among the musicians, shortly after they began playing. You can see it here; and searching YouTube for "Crissy Broadcast" will turn up clips others have sent in as well.
Friday, October 25, 2013
Sociopaths
The recent Congressional breakdown over funding the government suggests that today’s social “warfare” is not between Christians and Muslims, as at the time of the Crusades; or Catholics and Protestants, as during the Hundred Years War, or between white people and black people, as during slavery and the Jim Crow period following Abolition. It is not between Democrats and Republicans; not even between the rich and the poor. It is between, not to mince words, communitarians and sociopaths.
Communitarians consider
Sociopaths exhibit
Wikipedia cites definitions of sociopathic behavior as stated by the American Psychiatric Association:
But, oddly, sociopaths, like anarchists, are able to transcend their presumed near-total loathing for community and band together in sociopathic groups, dedicated to opposition to other social groups. Sociopathy is becoming institutionalized within ad hoc associations like the Tea Party.
Worse, because more insidious, sociopathic “values” like the seven characteristics listed by the APA are beginning to characterize official behavior, ranging from the presidential decision to assassinate suspected terrorists (and the inevitable innocent bystander) to a recent incident in my own local city, where police shot and killed an eighth-grader who was carrying a (borrowed) “toy” rifle.
According to the newspaper account, the toy is manufactured and distributed for use in indoor facilities where properly trained and armored participants shoot at one another for “sport.” Further, the weapon is deliberately made to resemble a military assault weapon, with the double result that it is apparently very popular among practitioners of the “sport,” and quite confusing to the police.
What kind of society provides facilities for the sport of pretend warfare? What kind of culture leads parents to believe this is healthy sport for their children? What kind of government encourages its police to fire first, investigate later? In my view, a sociopathic society.
The beast thrashes, tail in mouth, attempting to devour itself.
Communitarians consider
the connection between the individual and the community. While the 'community' may be a family unit, it is usually understood in the wider sense of interactions between a community of people in a geographical location, or who have a shared history or interest.[1] Communitarian philosophy is derived from the assumption that individuality is a product of community relationships rather than only individual traits.[Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Communitarianism]
Sociopaths exhibit
a pervasive pattern of disregard for, or violation of, the rights of others. There may be an impoverished moral sense or conscience and a history of crime, legal problems, impulsive and aggressive behavior.[Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antisocial_personality_disorder]
Wikipedia cites definitions of sociopathic behavior as stated by the American Psychiatric Association:
A) There is a pervasive pattern of disregard for and violation of the rights of others occurring since age 15 years, as indicated by three or more of the following:This definition pertains to individual behavior, and goes on to stipulate that
1 failure to conform to social norms with respect to lawful behaviors as indicated by repeatedly performing acts that are grounds for arrest;
2 deception, as indicated by repeatedly lying, use of aliases, or conning others for personal profit or pleasure;
3 impulsivity or failure to plan ahead;
4 irritability and aggressiveness, as indicated by repeated physical fights or assaults;
5 reckless disregard for safety of self or others;
6 consistent irresponsibility, as indicated by repeated failure to sustain consistent work behavior or honor financial obligations;
7 lack of remorse, as indicated by being indifferent to or rationalizing having hurt, mistreated, or stolen from another;[American Psychiatric Association (2000). "Diagnostic criteria for 301.7 Antisocial Personality Disorder". BehaveNet. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition, Text Revision. Retrieved 8 July 2013]
B) The individual is at least age 18 years.
C) There is evidence of conduct disorder with onset before age 15 years.
D) The occurrence of antisocial behavior is not exclusively during the course of schizophrenia or a manic episode.
But, oddly, sociopaths, like anarchists, are able to transcend their presumed near-total loathing for community and band together in sociopathic groups, dedicated to opposition to other social groups. Sociopathy is becoming institutionalized within ad hoc associations like the Tea Party.
Worse, because more insidious, sociopathic “values” like the seven characteristics listed by the APA are beginning to characterize official behavior, ranging from the presidential decision to assassinate suspected terrorists (and the inevitable innocent bystander) to a recent incident in my own local city, where police shot and killed an eighth-grader who was carrying a (borrowed) “toy” rifle.
According to the newspaper account, the toy is manufactured and distributed for use in indoor facilities where properly trained and armored participants shoot at one another for “sport.” Further, the weapon is deliberately made to resemble a military assault weapon, with the double result that it is apparently very popular among practitioners of the “sport,” and quite confusing to the police.
What kind of society provides facilities for the sport of pretend warfare? What kind of culture leads parents to believe this is healthy sport for their children? What kind of government encourages its police to fire first, investigate later? In my view, a sociopathic society.
The beast thrashes, tail in mouth, attempting to devour itself.
Sunday, October 20, 2013
The Dutch-American historical connection
From the vault: this was written last January, but for some reason never posted to the blog. It still seems to the point.
YESTERDAY I READ A BOOK confirming and explaining the connection I've long felt exists between Netherlands and the United States — a common mentality, you might say, a societal posture differentiating them from other nations. Not all other nations, perhaps; and not entirely: but a special orientation enabling a societal organization — "political," in fact — that underlies the social responsibilities enabling a social contract, written or not.
The book is in fact a pair of short essays by Geert Mak and Russell Shorto, 1609, The Forgotten history of Hudson, Amsterdam, and New York, published in 2009 in a handsome bilingual edition by the Henry Hudson 400 Foundation. Hudson arrived in New York harbor on his ship the Half Moon in 1609; the book was published as part of the events celebrating the 400th anniversary of that event.
Hudson was English, not Dutch, but he sailed on a commission from the Dutch East India Company, who hoped he would find a short route to Japan and China by sailing along the north Russian coast where the long summer days, it was thought, might melt the polar ice. He was four centuries too soon for that, as we know now, and before rounding the north cape of Norway turned back, crossed the Atlantic, and sailed to what is now Virginia to visit his friend John Smith in the colony there; then looked into first the Delaware river, then what's now the Hudson, hoping for a passage through the North American continent to the Sea of Japan.
(Not as ridiculous as it seems today, Shorto points out. At the time most navigators and cartographers thought that Ptolemy's ancient estimate of the size of the earth was correct; this would have placed Japan about where Ohio is.)
Hudson sailed up his river as far as present-day Albany before the river proved entirely fresh water, not salt, dashing that hope. But he explored the banks, and reported back to the Company that the fields were fertile and well-supplied with game. Before long the Dutch were sending colonists to stake out their own territory north of England's doomed Roanoke colony, and New York was Nieuw Amsterdam until 1664, when the English finally claimed the city at gunpoint.
By then the city had begun to develop qualities that characterize it still, qualities that early set it apart, Shorto writes, from "Boston, Hartford, or any other city in English North America." And what were those qualities? "Free trade and an immigrant culture," the features that enabled Amsterdam's rise in the late 16th and the 17th century as the most important, richest trading city in the world. The shipping companies were owned by a Dutch innovation, stock companies, not a monarchy; risk was shared as were returns; and the co-operation this necessitated was underwritten by a relatively liberal, tolerant view of differing social values.
Amsterdam, with its busy seaport, had already been attracting refugees from the religious wars in Germany and France, and the suppression of the Jews in Spain. "In an age of religious strife, it was almost universally held that a nation should be of one people and one faith," Shorto writes.
Intolerance was thus official policy in England, Spain, France… but not in the Dutch nation. There, tolerance became a topic of political and religious debate. Tolerance was adopted as a policy — not as a grand ideal, but as a way to deal with the mixed character of the population.The Union of Utrecht, for example, declared as early as 1579 that "each person shall remain free, especially in his religion, and that no one shall be persecuted or investigated because of their religion."
As a result, Shorto argues, the Dutch colony in New York was a mixture of ethnic and religious strains from the beginning, approaching common problems and decisions in the spirit of common consent. "Even as early as the 17th century," Mak writes,
the Dutch had an uncontrollable inclination to assemble and to "polder" or debate until consensus is reached. This inclination based on the collective decision-making they were accustomed to as they worked together to reclaim their wetlands… Everything revolved around the art of persuasion, convincing others through debate.The technique has its drawbacks, of course: it requires an educated, articulate, and probably fairly small body of discussants; and it takes time to arrive at its consensus. But it's a commendable procedure, and no doubt served as a model to the "Founding Fathers" as they themselves debated the form of the new government to follow the American Revolution.
Thursday, October 17, 2013
Staff of Life

Eastside Road, October 16, 2013—
NEARLY TWENTY-FIVE years ago, in 1989, the noted home baker, teacher, and cookbook author Marion Cunningham, who was based in the San Francisco Bay Area, used to get together with Amy Pressman, who had a bakery in Pasadena at the time, to spend hours discussing various baking ideas, problems, and techniques. Eventually they decided that if they learned so much about baking from their casual meetings, other bakers would appreciate the opportunity to discuss the pleasures and mysteries of baking, too.I quote that from the website of the Bakers Dozen, the organization that grew out of their conversations a few months later. I often refer to this as my wife's "professional organization," as almost everyone knows what such a thing is, but that's misleading: one of the marvelous things about the group is that included from the very start amateurs — "home bakers" — as well as professionals.
We have belonged to the group, Lindsey and I, from the beginning. I am hardly even a home baker, though for a few years I did bake our daily bread, which I suppose qualifies me a little bit for membership, beyond my other, more important qualification, as the Lovely Little Husband of a woman who after all was named Pastry Chef of the Year back when she was still in the traces at Chez Panisse.
I have always been struck by the curious, perhaps unique combination of generosity and discipline that characterizes so many of the bakers I have known. Whether working at savory or sweet, bread or pastry, the baker must be focussed and attentive. Success depends on discipline and repetition. One thinks of the typical pastry chef as being a bit of a control freak, and indeed meticulous care for detail is central to success in the field. Temperature and proportion require extreme care, particularly in a commercial bakery or restaurant where consistency is important, perhaps even crucial.
But every baker knows that one's ability to control goes only so far. The weather; irregularities in commercial supplies; even fluctuations in room temperature or humidity can influence the outcome of any day's work. The baker, like the baseball player, lives at the cusp of control and circumstance. Perhaps this contributes to qualities I've often noticed in bakers, if not perhaps baseball players: a certain humility, a cheerful degree of resignation; a wonderful combination of generosity and frugality; an enthusiastic commitment to their work. I come away from every meeting of the Bakers Dozen with renewed optimism about humanity because of the evidence it provides of these qualities.
 |
|---|
| Craig Ponsford addressing the Bakers Dozen |
This week we were particularly interested in a presentation by Craig Ponsford, the California baker who famously won the gold medal at the Coupe du Monde de la Boulangerie in Paris in 1996, an event as epochal as the celebrated breakthrough of California wines twenty years earlier at the "judgment of Paris."
At the time, Ponsford was a founding partner in Artisan Bakers, a bread bakery he'd opened in Sonoma, California, one of a number of bakeries which had opened in the Bay Area in the wake of Steve Sullivan's Acme Bakery, which had pioneered the great second generation of Bay Area breads. (Larraburu and Toscana, much larger commercial bakeries, had established the first.)
Although he and Artisan parted company a while back, Ponsford is still an active baker. You can buy his breads in San Rafael at Ponsford's Place, usually on weekends. This is undoubtedly a boon to locals, but it seems to me Ponsford's really significant contribution to the art of baking, these days, is through his work in consulting to millers, and publicizing their own work.
No matter how competent the baker, it will always be the flour that makes the bread, and Ponsford is currently hard at work spreading the word about flour. This is particularly significant now, when there is so much talk about gluten and its digestibility in the human diet. The flour we have all been fed, whether in home-baked bread, bread baked in small local bakeries, or good old Cellophane-wrapped sliced white sandwich bread, has for the last century or so been the product of huge corporate millers.
These mills indulged and encouraged the popular taste for white flours and breads. According to Ponsford, over a century ago a process was developed which "tempered" wheat grain, softening it in water to encourage it to sprout just enough to make it easier to remove the outer husk that protects the pure white endosperm. This was done to simplify the production of pure white flour, but it accelerates the kernel's development of gluten. Since the tempering process was quickly adopted by most industrial millers, today's flours contain a higher gluten content, as can be seen in industrially baked breads.
The human digestive tract evolved to find nourishment in grains — more accurately, I suppose, grains and humans evolved together, grains profiting from human agriculture to flourish in ever newer climes and soils, humans profiting from grain's adaptability and ease of portability and storage. But the grain we evolved with was whole: not bran, not endosperm, not germ: the entire grain.
Ponsford explained that flour, like sugar and even milk, is processed industrially by separating it as soon as possible to its simplest states. Bran, germ, and endosperm are separated; industrial "whole-wheat" flour is simply bleached white flour with a certain amount of germ and bran mixed back in. Similarly, brown sugar is refined white sugar with molasses mixed back in; "whole" milk is non-fat milk with butterfat mixed back in.
When I was a kid we ate three kinds of bread: the usual American industrial sliced bread, also known as "balloon bread" or, by synecdoche, "Wonder bread"; "French" bread, usually Franco-American, still baked in Santa Rosa, our local city; and homemade bread, for which my mother used I don't know what commercial flour, probably General Mills. She used her own yeast-based starter, kept on a kitchen windowsill where it often smelled unpleasant, and I remember the slow progress of her bread from a light, fluffy loaf, full of holes, through a brief period when it seemed to be like "normal" bread, to a final stage when it became impossibly dense and chewy.
The French bread was usually sliced, spread with margarine, sprinkled with garlic salt, and warmed in the oven, and I thought it was a treat.
The commercial sliced balloon bread was another matter. I usually ate it by nibbling off the crust all round the slice, then folding the remaining white slice in half, folding that in half again, compressing the result between the palms of my hands, and repeating the process. The result was a leathery slightly sour-tasting thing, more or less dark depending on the state of my hands. It wasn't very tasty, but it was better than sliced bread. It was of course the result of otherwise unameliorated gluten.
PONSFORD CURRENTLY CONSULTS to Community Grains, a company in Woodland, California, which finds responsibly grown grains and mills them in a traditional (i.e., pre-tempering) manner. The resulting flours (and polenta) are whole-grain: the entire kernel is ground all at once, without separating germ, bran, and endosperm. The resulting flours, Ponsford says, are more readily digested than those resulting from conventional industrial milling, because — this is my explanation, not his — they are in better balance: properties of gluten which can cause digestive problems are offset by properties in other parts of the grain which interact with the gluten.
Of course support for this conclusion is largely deductive so far: I don't know to what extent scientific procedures have been brought to the investigation. But there's no question that diseases now widespread in "developed countries" have dietary correlations: diabetes, obesity, and intestinal disorders obviously so; and that there's a demonstrable correlation between the appearance and increase of these diseases and the further reliance, in the areas in which they appear, on industrialized production of flours and sugars.
 Ponsford told me that it was Community Grains, up in Woodland, that had milled the wheat recently harvestedd by our friends Andrea Crawford and Robert Dedlow, the proprietors of Kenter Canyon Farms. Andrea was a gardener and forager for Chez Panisse many years ago, before the couple relocated to Southern California to raise produce for the restaurant-and-carriage trade there. Andrea has long been an enthusiastic home baker, and when they had the opportunity to plant fifty acres of flat, fertile Central California coastal-influenced farmland near Hollister, they decided to plant wheat.
Ponsford told me that it was Community Grains, up in Woodland, that had milled the wheat recently harvestedd by our friends Andrea Crawford and Robert Dedlow, the proprietors of Kenter Canyon Farms. Andrea was a gardener and forager for Chez Panisse many years ago, before the couple relocated to Southern California to raise produce for the restaurant-and-carriage trade there. Andrea has long been an enthusiastic home baker, and when they had the opportunity to plant fifty acres of flat, fertile Central California coastal-influenced farmland near Hollister, they decided to plant wheat. In the meantime Andrea had been developing her own recipes and methods. Last May we had lunch at their house, in the hills above Glendale, and were impressed with the results — though at the time she was using commercial flour, as their own harvest hadn't yet come in.
But last week she was able to sell her own bread, and their own grain and flours, at the Santa Monica and Hollywood markets. The bread at the top of this blog post is hers, bought last Sunday morning in Hollywood and keeping well into this week. The texture is even, the crust pleasantly chewy, the flavor well focussed, with that intensity that comes from well-proofed dough.
I'm glad to see her bread on the market, and glad to see it getting the attention it deserves in the Los Angeles Times (where it was written about by no less a figure than David Karp, who maintains the "market watch" column at that newspaper. We know him (my first-person-plural is not editorial: it always includes Lindsey) as the Fruit Detective, a man of immense erudition and enthusiasm; I'm glad to see him extend this from orchards to wheatfields.
California used to produce a large percentage of the nation's wheat, before economies of scale encouraged relocation to the plains states. The area around Woodland, in Yolo county, used to be wheatfields; my grandfather, who was born in Geyserville in 1883, remembered living there on the family farm in the 1890s, and watching the huge teams of horses drawing combines across the fields, and, soon enough, massive steam-engines replacing the teams.
Here in Sonoma county our friend Lou Preston (Preston of Dry Creek), who makes a mean loaf of bread in his Alan Scott-inspired wood-fired oven, is also growing wheat on his biodynamic farm. In cold weather we cook our "bog-man cereal" using his wheat, which we buy at the farm. There is no shortage of serious bakers of bread hereabouts, Ceres knows: and, of course, we have our own commercial bakeries in Healdsburg, of which our favorite is naturally the Downtown Bakery and Creamery, which Lindsey and our daughter Thérèse founded with co-founder and present owner Kathleen Stewart back in 1987. Downtown Bakery & Creamery supplies our daily bread, though we enjoy Lou's, and Joe Ortiz's bread at Gayle's Bakery down in Capitola, and of course Steve Sullivan's bread at Acme (many of us think of him as the founding father of the bread revival hereabouts), and, now, Andrea's, when we're in Los Angeles.
But all this has made me think it's time for me to put my hand back in — particularly with the availability of local flours. Lou sells his flour, and there's a couple of pounds in the pantry. Maybe I'll get back to work.
Monday, October 14, 2013
Einstein, again
Eastside Road, October 14, 2013—
WHY WOULD ANYONE in his right mind spend hundreds of dollars and travel thousand of miles to see Einstein on the Beach four times in eighteen months — unless it were one of the great moments in the century of art from, let's say Symbolism to Postmodernism?So there we were again, two nights ago, in center seats in the fourth row of the balcony at the Dorothy Chandler Pavilion in Los Angeles's Music Center, sitting among an enthusiastic and attentive audience for the most part. (I wasn't able to see how the higher-priced section downstairs looked: I'm told there were empty seats.)
We saw the premiere (not counting an earlier preview) of the current traveling production of the Robert Wilson-Philip Glass-Lucinda Childs opera in Montpellier in March 2012; I wrote about that here and here. A year ago we saw it in Berkeley, as I mentioned here.
Then in January of this year we flew to Amsterdam, as I mentioned here. At the time we'd planned that trip, the Amsterdam performances were thought to be the final performances on the tour, but subsequent bookings were signed for Hong Kong, Melbourne, and this month's in Los Angeles. Perhaps the tour will go on forever: I almost hope so.
In each of the last three dates we've made with Einstein we've introduced friends and/or family to the opera, making it a double-date of sorts. I feel it almost an obligation to introduce others to this event, for a number of reasons, all of which I've already written about, over and over. I think I finally said it best in the most recent post, after the Amsterdam performance, when I tried to deal with
the question "Well, what is the opera about? In a nutshell, it's about the Twentieth Century, the historical process from steam trains like those Einstein rode in his youth, when he profited from the experience to analogize his theories on the relativity of time for popular understanding, to the age of the space ship.Having already written so much on the opera itself, I'll just comment on a few impressions from Saturday night's viewing. The Los Angeles installation of this traveling production seemed faster to me, though my companion assures me the running time was almost exactly what it's been before. Time seemed to pass more quickly: the opera seemed, well, defter. The sound seemed richer, too. The wonderful saxophone solo under Act IV scene 1, the "Building" scene, was counterpointed with percussion I'd not noticed earlier, and with a flute more prominent than I'd remembered.
But I almost completely gave up on commenting on the main thing the opera is about, which is Theater. As the ancient Greek plays are about cosmic things, examining human dilemmas in cosmic contexts, so are Robert Wilson's. The opera is about Theater, and Time; and it uses theatrical time, and plenty of it — over four hours, in which the audience is free to roam if necessary — to examine those two notions.
Of course one of the things we'd already noticed in these repeated participations at Einstein is precisely that: the changing impressions the production makes as one gains familiarity with it. It's so rich and complex that many events or moments or sounds become evident, on repeated viewing/hearing, that were very likely there all along, and simply sidelined, as it were, by one's attention having been fixed elsewhere. That, of course, is one of the things the opera is "about."
Another thing about the Los Angeles production: the lighting seemed subtler, richer (that word again), even more effective. There were more colors, and many of them were more delicate. The band of light ending Act III scene one — the second of the two extended dance scenes — was particularly affecting, bringing James Turrell to mind — a particularly appropriate quality in Los Angeles.
Even the dramatic content of the show seemed affected by the geographical culture of its locaton. The second trial scene, which seemed so Kafkaesque in Amsterdam, passed by almost as entertainment in Los Angeles. So, too, the first trial scene, with its dialect spoof of feminism, borrowed the movie-and-TV context to become less potentially objectionable, more simply diverting.
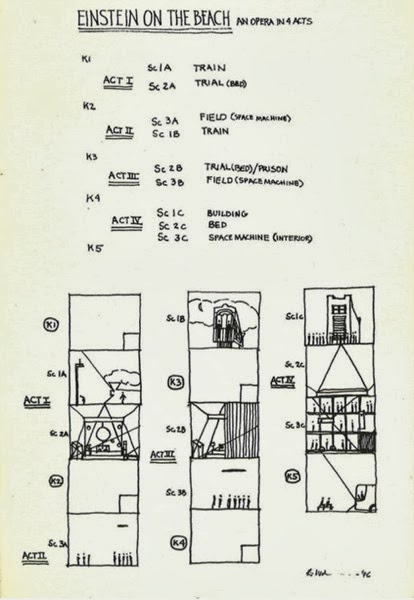
I've reproduced here — a Los Angeles Opera spokeswoman invited me to lift it from their website — Wilson's drawing which serves as a non-verbal aide-memoire to the opera's structure. It repays attention, I think, as the structure is fascinating: three scenes (Train, Trial, Space Machine) repeated across four acts which are separated by "knee play" entr'actes. So the opera presents the idea of Relativity (encapsuled in the famous train analogy, showing that time passes differently for the passenger on a train than for a stationary observer of the train); then the effects or the expressions of relativistic concepts on social or political situations which imperfectly confront them; then the aspirations of 20th-century humanity to harness those concepts to technology which might lead them out of the century and its oppressions.
Plenty to think about here. It would be so interesting to spend a weekend in the country with the friends and family we've introduced to Einstein, talking about it. That, I think, would be the best possible form of criticism: conversation in repose, following experience in intensity.
Tuesday, October 08, 2013
Home is Here
| Home is Here. By Sidney Meller. New York: The Macmillan Company, 1941. |
Eastside Road, October 6, 2013—
I POSTED HERE the other day — well, a month ago, I see now; time does get past me — some comments on a novel by my favorite English teacher, Sid Meller, a man who taught me what to look for in novels, and who encouraged me in my own juvenilia. Meller's first novel, Roots in the Sky, was a "chronicle novel," rather a sprawling one brought to rather a sudden and arbitrary conclusion aided by a sudden street accident. The narrative hung on the immigrant orthodox Jewish subculture in San Francisco, from say 1910 into Prohibition.I recently read Meller's second (and last) novel, a more successful book to my mind, written I suppose in the late 1930s, perhaps as late as 1940. It is another novel about an immigrant family, but more the opposite corrective to the earlier novel than its similar. Unlike Rabbi Drobnen in Roots in the Sky, the Alano Dorelli is eager to assimilate, or at least to take his place in the thriving, upwardly mobile milieu he finds on Telegraph Hill just after the 1906 earthquake.
It takes a year or two and perhaps forty pages for his wife Lucia to arrive from the shores of Lake Como, and she is never as sanguine as her husband about leaving the traditions and the simplicity of their earlier paisano life — but by the book's end it is she who has beat yankee exploitation and crass politics, leaving him finally respectful of her reluctant determination.
The plot hinges on her quarrel with the owner of the sandstone quarry whose scar still shows on the eastern and southern flanks of the Hill. One house after another has tumbled into its maw as his operations have continued, following his father's and grandfather's work stretching back to the Gold Rush days. Much of the novel concerns the different responses to the problem among the Italian, Spanish, and Irish immigrants forming a sometimes uneasy community.
As in his earlier novel, Meller also investigates the differing visions of the younger generation, the first-generation Americans, as they respond to changing social and technological conditions and to the sometimes fixed, sometimes bewilderedly floundering doings of their parents.
A site on the always surprising Internet has yielded four reviews of Home is Here. I particularly liked that of Henry C. Tracy, published in Common Ground:
…it is in Lucia's mind and spirit that the drama of this finely-wrought book emerges and moves toward a climax—a spirit often weak and fluctuating, a mind often foolish but essentially sound. It is her night school teacher, a bit stilted but wise, who tells her that "America is becoming."Home is Here is aware of the more skeptical, perhaps even cynical views of America in such books as The Grapes of Wrath, but takes a completely different view of things, preferring challenge to problem, enterprise to despair. I remember Meller assigning Modernist titles in his class on the novel — it was here I first read Joyce — but he included Robert Nathan's One More Spring as well. Home is Here would have made a fine Frank Capra movie, though I don't see Henry Fonda as Alano.
No author has better told the inside story of neighborhood groups of new Americans from Lombardy, Genoa, Sicily, Grenada, with some Irish and Yankee stock intermingled, sinking differences in he American way…
World War II changed everything, of course; the ease and the fun and the grass-roots power available even in hard times, through the simple efforts of a people forced to rely on themselves, gave way to the stress and distractions in a society controlled by faceless corporate forces. The novel is long out of print, but copies are available at online used-book sites. It will strike many contemporary readers as quaint, I suppose, but its quiet optimism and good humor are qualities we'd do well to recover in the social and political climate of today's America.
Sunday, October 06, 2013
Buried Child
| Buried Child. By Sam Shepard, directed by Loretta Greco. San Francisco: The Magic Theater; seen September 27, 2013. |
Eastside Road, October 6, 2013—
WE CLOSED OUT last week's three-play marathon in a venue we haven't visited for years, the veteran Magic Theater in San Francisco's Fort Mason. John Lion founded the company in 1967, according to the Wikipedia article I'm consulting, in the old Steppenwolf bar down on San Pablo Avenue in Berkeley. I remember seeing at least one of Michael McClure's "Gargoyle Cartoon" there, but Lion moved the company to San Francisco in the early 1970s, finally settling in the present location in the middle of that decade.McClure was a (or the ) resident artist at the Magic for eleven years, giving the company a unique blend of poetry, sometimes violent energy, and what I think of as an anti-intellectual philosophy. I have often wished for an opportunity to study a number of his plays, in performance of course, in a single season, but he seems to have fallen out of favor locally, and I make do with vague memories of The Blossom, or Billy the Kid; The Beard; the Gargoyle Cartoons of course; Gorf; and Josephine The Mouse Singer.
At about the time the Magic moved into its current Fort Mason digs, the already notable American playwright Sam Shepard succeeded McClure in residence. Both men were born in the midwest; both were Californians by the time they were twenty or so; both have keen ears for the vernacular and a healthy respect for the meat of human experience as well as the brain. They make a fascinating pair; come to think of it, a McClure-Shepard festival would be another fascinating experience.
(Wouldn't it be marvelous if the Bay Area's rich theater community — rich in all but money, alas — could join forces to mount such events!)
I think we have seen only one other Shepard play: Fool for Love, which was splendidly performed in May 2012 by the community Main Stage West in Sebastopol and subsequently repeated at the Imaginists in Santa Rosa. Fool for Love premiered at the Magic in 1983; Buried Child had appeared five years earlier and is, to my mind, a less successful piece — because less resolved, a result of its greater complexity and ambition.
Some of the play's irresoluteness may be the result of its writing. Shepard revised the script for its 1995 revival in Chicago, and Robert Hurwitt has stated the Magic Theater production used that revision; but the Magic itself calls this a "Legacy Revival" celebrating the playwright's 70th birthday (November 5) and Magic's own role in premiering so much of his work. I haven't read the play; I don't know if there is, or can be, a definitive state of the script.
In any case we saw Buried Child in the context of two other plays, as the previous two posts here indicate, and that context had much to do, I think, with the powerful immediacy of Shepard's script even in what seemed to me an unevenly directed production. Rod Gnapp was compelling as Dodge, the surly, bitter, authoritative, dying father of a mythically dysfunctional farm family somewhere in the American heartland. But his presence was so strong, so central to the production, that other members of the cast, capable as they were, too often moved on the margins.
Shepard invites the problem. Halie, Dodge's wife (Denise Balthrop Cassidy), enters through several minutes of lines spoken offstage. Bradley (Patrick Kelly Jones), the amputee son, spends much of his time lying on the couch, arm across his face. Tilden (James Wagner), the other son, makes his most effective contributions to the drama offstage.
By contrast, Vince (Patrick Alparone), Dodge's errant grandson, making an unforseen visit with his girl friend Shelly (Elaina Garrity), hold the center of the stage, insisting on a present reality, forcing it into the decaying monochrome of this household of suppressed emotion.
Jane Ann Crum's program notes on the play enlarge on the nature of the theatrical reality in Shepard's construct:
One of the primary differences in Shepherd's [sic] dramaturgy is what could be called tears in the fabric of reality.Other critics have commented on the Shepard esthetic as being an expression of Postmodernism: but in fact Buried Child seems to me to be a perfectly logical and foreseeable continuation of the curve of realistic drama from Ibsen and Shaw through O'Neill and Williams to Shepard and Stoppard. Yes, there are rents and tears in the fabric of reality; we have come to find these flaws more real than the imagined and manufactured reality of the fabric, which maintains its integrity only when external realities are ignored.
The arresting moments in Shepard recall those in Shakespeare, who is so fascinated by the irrational events which like Epicurus's swerves define, distort, and impel the forces and trajectories we humans so desperately want to be rational and orderly. It was profoundly shocking to be confronted with the buried child of Shepard's play, a day after having dealt with Leontes' figurative burial of his own.
Too, Vince and Shelly — quite strongly performed here — recalled Clyde and Bonnie, seen only two days before, living on a disorienting cusp of inner and external realities, torn between context and the moment. (They also recall May and Eddie, if Fool for Love. As there are only so many plots — seven, many pretend — so there are probably only a small number of characters.)
One thing is clear to me, after these three nights of theater: Shepard's work, necessarily imperfect though it may be on the stage where it is consigned to its public moment, is deep with undertones and rich in scope, a significant development in American literature and world stage.
Thursday, October 03, 2013
A Winter's Tale
| A Winter's Tale. By William Shakespeare, directed by Patricia McGregor. Orinda: California Shakespeare Theater; seen September 26, 2013. |
Eastside Road, October 3, 2013—
COMPARISONS BEING ODOROUS, as Dogberry says, I won't bring up productions of Shakespeare recently seen in Ashland here: I'm writing today about a very different order of things.A Winter's Tale, one of Shakespeare's more problematic plays, was formerly rarely given, but seems to have become popular: we've seen it now five times in the last six years. Two main difficulties may have been responsible for its long retreat from the stage: the unprompted and violent swings of mood in the principle character, Leontes; and the alternations of high tragedy and low comedy, which tend to tear the play apart in uncalibrated productions. Like Cymbeline, the play's an example of Shakespeare's idiosyncratic combination of realism and abstraction.
As so often, he examines in this play the effect of a sudden loss of reality: a rage, or a colossal error, or an unforeseen coincidence — a chance calamity that changes everything for everyone, bystanders as well as perpetrators, the innocent as well as (or even more than) the "guilty." But what are the perpetrators guilty of ? in most cases, they too are the victims of the kind of exception that follows when the natural order of things takes a sudden, inexplicable swerve. Everything in Shakespeare's world — his natural world and that of his society — is tenuous.
Patricia McGregor's direction of the play had its merits and its flaws. For me, on reflection, the flaws outweighed the merits: particularly the idea of involving the audience through direct address from the stage, even invitations to participate on the stage. As the play opened, a traveling band of players, acrobats, and fortune-tellers, looking vaguely medieval but with diction recalling Second City improv routines and accompanied by an Airstream-like camper-trailer, cajoled the audience into banter which recurred at the beginning of the second act and returned at the close. This seemed miscalculated in the outdoors amphitheater, colder than any Winter's Tale needs for its setting.
But another directorial concept worked amazingly well: the cast was collapsed onto a seven-actor ensemble with every role double-cast. This streamlined the scenes in Bohemia, which can lapse into irrelevant clowning, losing the play's drive toward its final stroke and resolution; it also very neatly underscored the schizophrenia at the heart of Shakespeare's vision.
Nowhere better than in the amazing performance of L. Peter Callender as both Leontes, who directs the abandonment of his infant daughter on a coastal rock in Bohemia, and the Shepherd who finds her and raises her as his own child. He found deep humanity in each of these roles, and nicely detailed individuality as well; but the two characters are so different it was hard to force myself to realize they were played by a single actor.
The same can be said for Omoze Idehenre, who played both the wronged queen Hermione and the lovestruck shepherdess Mopsa; and for Tristan Cunningham, both Perdita and Emilia; and Christopher Michael Rivera, who was a noble Antigonus, a conniving Autolycus. Aldo Billingslea, Margo Hall, and Tyee Tilghman round out the cast.
Most of the cast had played in a previous Cal Shakes production this season, Spunk: we didn't see that show (though it sounded promising), but apparently it too involved audience participation and an all or nearly-all black cast. It may have worked better, presenting material closer to the experience of today's audience.
On the other hand, having seen that production may have helped the audience at A Winter's Tale. I myself, knowing the play from its script and from previous more conventional productions, found the framing device irrelevant and distracting, even confusing at times. The reduced cast made it necessary to cut and collapse much of the fourth act, set in Bohemia; and to skip the first scene of the fifth act, since virtually Shakespeare's entire cast is assembled. Here again the traveling players try to explain matters to the audience; here again I find myself in a state of confusion.
I should concede that we saw the production in a preview; some production elements were clearly not completely resolved. In the last analysis, though, I think few modern adapters and presenters of Shakespeare calibrate the play-to-audience configuration better than does the Bard himself, and I wish more contemporary productions would trust his book.
But much of the time I was gripped by the rage, the jealousy, the love, the remorse, the understanding, and the forgiveness that animate this marvelous play. The reason for this is simple: the power of Shakespeare's words, and the clarity and conviction of the actors' speech. A number of moments will stay with me.
A Winter's Talecontinues at the Bruns Memorial Amphitheater, Orinda, through October 20, 2013.
Bonnie and Clyde
| Bonnie and Clyde. By Adam Peck, directed by Mark Jackson. Berkeley: Shotgun Players; seen September 25, 2013. |
Eastside Road, October 3, 2013—
A quick look at the calendar shows sixteen plays seen so far this year (and three operas), and recently I've been complaining a lot about what we've seen. I should make it clear, once again, that I post these notes not as serious critical reviews, merely as personal opinions. For years I worked as a critic on the staff of the Oakland Tribune, mostly on art and (concert) music but occasionally also covering theater. During that time I felt strongly that a part of a newspaper critic's responsibility is to suspend his own likes and dislikes.
I always liked Joseph Kerman's definition of criticism: "[T]he study of the meaning and the value of art works." (Contemplating Music: challenges to musicology, Harvard University Press, 1986). The newspaper employed me to do just that, but — I felt — to do it from a neutral perspective. My responses; my brain; the publisher's voice. I was paid, pretty well I thought; and I was provided with entrance to theaters, concert halls, museums; and even with entry to conversations with artists and performers I would normally never be able to meet as a private individual. The least I could do in return was to suppress my own ego and tastes, as much as possible while retaining presence.
But The Eastside View is not a newspaper: it's a personal blog, expressing my own viewpoint from here on Eastside Road, where I can read and write among my books and scores, journals and files — and, through the Internet, plenty of reference when I want it. And of course there's another matter: I'm pushing eighty; there's less time to waste; I need do and think and write only as I choose.
All that said — and it's been a lengthy and perhaps self-indulgent precede — what about last week's theater? Bonnie and Clyde, by Adam Peck, was a one-act, 90-minute scene for two actors, Megan Trout and Joe Estlack, cutting between intimate conversation between them and flashbacks and -forwards, dramatically isolated with light and sound, providing the context for the scene.
Is there anyone who doesn't know the story of Bonnie and Clyde, the small-town bank robbers who shot their way through Texas and Arkansas in Arthur Penn's movie (1967) burned them into a second generation's consciousness, and must remain for many the nearly official account of their career. When that movie came out I participated in a panel-discussion review on KQED, with David Littlejohn, Tony Boucher, and someone else. (In those days KQED was happy to give fifteen or twenty minutes of prime time to such a discussion; what a time that was!)
It was my view then that the movie was unspeakably violent; that in fact it promoted violence as beauty, and that ultimately that would not be a good thing. I still feel the cult of violence has led the American vernacular culture into a thicket, and that there can't help but be a connection between the omnipresence of violence, and of its beauty and power, in games, television, film, books, and popular music, and the gun mania, mass shootings, remote assassinations, and road rage that are so present in American life.
But the story of Bonnie and Clyde is a potent one, underneath whatever stylistic treatment it receives. And if Penn's film distracted me from that story, with its big-screen beauty and graphic final shootout, Peck’s play, in Mark Jackson’s direction for Shotgun Players, returned me to it. I was given a corrected view of its historical specificity: I kept thinking that Bonnie and Clyde were of my father’s generation, that they lived and died within a few dozen miles of his childhood home. My parents, in their twenties, undoubtedly read of Bonnie and Clyde’s exploits in the newspapers, saw the no less graphic black-and-white photos of their corpses in their pages; perhaps saw footage in the newsreels.
(Facsimiles of contemporary newspaper coverage were posted on the lobby walls at Shotgun, further enhancing this contextualization of the story.)
I came to see the story of Bonnie and Clyde as parallel to another American legend of nearly the same time, also seen recently in a theatrical version: The Grapes of Wrath. Once again I was reminded of the communitarian value essential in theater. At its best, public drama, from the time of the Greeks, exists to present, to examine, perhaps even to explicate the workings of Nature and Society for an audience often denied, by the distractions and pressures of daily life, the luxury of their own private meditations on the human condition.
I write these sentences eight days after seeing the play, and express views that have developed since leaving the theater. The performance itself was arresting — no pun intended — both for the acting and the setting. Megan Trout’s Bonnie was certainly reminiscent of Faye Dunaway’s, but it was no impersonation of that performance: it had depth and detail of its own, a wistful quality within the hardened realism enforced not only by the immediate situation but by the nature of the time and place that formed her character.
Joe Estlack was at first sight less imposing as Clyde Barrow, too diffident and meticulous to suggest the rogue murderer, and secondary to the strength of Bonnie’s role as written in the script. In retrospect, though, his enactment has grown in my mind, offering a credible complexity, revealing the (possibly misplaced) idealism and sense of failed justice that provoked his actions.
Robert Broadfoot’s set design worked fine for me: a no-fourth-wall anonymous barn, its timbers perhaps too new, isolated in a countryside that could be anywhere, spacious enough for the couple to split into individuals, claustrophobic enough to isolate them from the society that formed them and that, by rejecting, they enrich with their myth.
Ultimately it's that mythic quality of the story of Bonnie and Clyde that Adam Peck's play summarizes, in its unique crosscuts of immediate present detail with glimpses of the months-long action of the saga. Peck's play manages to hew to Aristotle's three unities (action, time, place) while tapping outside elements necessary to his contextualization, and Jackson's direction realized that aspect of the play effectively in Berkeley's Ashby Avenue theater.
Trapped in their barn, Bonnie and Clyde live in the moment, aware it is among their last moments. To my parents that moment was the present; to me it is both theirs and ours, and the figurative, metaphorical meaning of that moment is powerful and relavent to the present.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)